145. Binary Tree Postorder Traversal
Medium
Given the root of a binary tree, return the postorder traversal of its nodes' values.
Example 1:

Input: root = [1,null,2,3] Output: [3,2,1]
Example 2:
Input: root = [] Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [1] Output: [1]
Example 4:
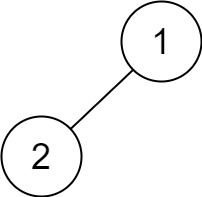
Input: root = [1,2] Output: [2,1]
Example 5:
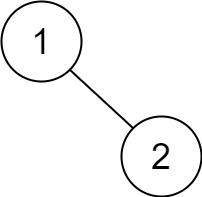
Input: root = [1,null,2] Output: [2,1]
Constraints:
- The number of the nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 | /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); if(root==null) return list; TreeNode H = new TreeNode(0); H.left = root; TreeNode p = H, pred, n1, n2, n3; while(p!=null){ if(p.left==null){ p = p.right; }else{//p.left!=null pred = p.left; while(pred.right!=null && pred.right!=p) pred = pred.right; if(pred.right==null){ pred.right = p; p = p.left; }else{ n1 = p; n2 = n1.left; while(n2!=p){ n3 = n2.right; n2.right = n1; n1 = n2; n2 = n3; } n1 = p; n2 = pred; while(n2!=p){ list.add(n2.val); n3 = n2.right; n2.right = n1; n1 = n2; n2 = n3; } pred.right = null; p = p.right; } } } return list; } } |

No comments:
Post a Comment