987. Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree
Medium
Given a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes values.
For each node at position (X, Y), its left and right children respectively will be at positions (X-1, Y-1) and (X+1, Y-1).
Running a vertical line from X = -infinity to X = +infinity, whenever the vertical line touches some nodes, we report the values of the nodes in order from top to bottom (decreasing Y coordinates).
If two nodes have the same position, then the value of the node that is reported first is the value that is smaller.
Return an list of non-empty reports in order of X coordinate. Every report will have a list of values of nodes.
Example 1:
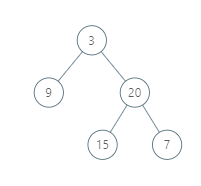
Input: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]] Explanation: Without loss of generality, we can assume the root node is at position (0, 0): Then, the node with value 9 occurs at position (-1, -1); The nodes with values 3 and 15 occur at positions (0, 0) and (0, -2); The node with value 20 occurs at position (1, -1); The node with value 7 occurs at position (2, -2).
Example 2:
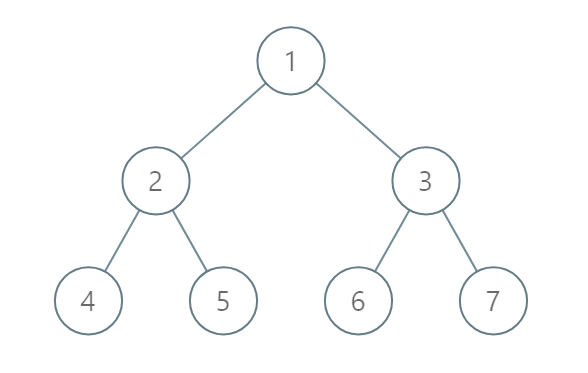
Input: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7] Output: [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]] Explanation: The node with value 5 and the node with value 6 have the same position according to the given scheme. However, in the report "[1,5,6]", the node value of 5 comes first since 5 is smaller than 6.
Note:
- The tree will have between 1 and
1000nodes. - Each node's value will be between
0and1000.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 | /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { Map<Integer, Map<Integer, List<Integer>>> map = new TreeMap<>(); public List<List<Integer>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode root) { helper(0, 0, root); List<List<Integer>> lists = new ArrayList<>(); for(Map.Entry<Integer, Map<Integer, List<Integer>>> m : map.entrySet()){ List<Integer> col = new ArrayList<>(); for(Map.Entry<Integer, List<Integer>> e : m.getValue().entrySet()){ List<Integer> list = e.getValue(); Collections.sort(list); col.addAll(list); } lists.add(col); } return lists; } void helper(int x, int y, TreeNode node){ if(node==null) return; if(!map.containsKey(x)){ map.put(x, new TreeMap<>()); } if(!map.get(x).containsKey(y)){ map.get(x).put(y, new ArrayList<>()); } map.get(x).get(y).add(node.val); helper(x-1, y+1, node.left); helper(x+1, y+1, node.right); } } |
No comments:
Post a Comment