133. Clone Graph
Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph.
Return a deep copy (clone) of the graph.
Each node in the graph contains a val (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> neighbors;
}
Test case format:
For simplicity sake, each node's value is the same as the node's index (1-indexed). For example, the first node with val = 1, the second node with val = 2, and so on. The graph is represented in the test case using an adjacency list.
Adjacency list is a collection of unordered lists used to represent a finite graph. Each list describes the set of neighbors of a node in the graph.
The given node will always be the first node with val = 1. You must return the copy of the given node as a reference to the cloned graph.
Example 1:
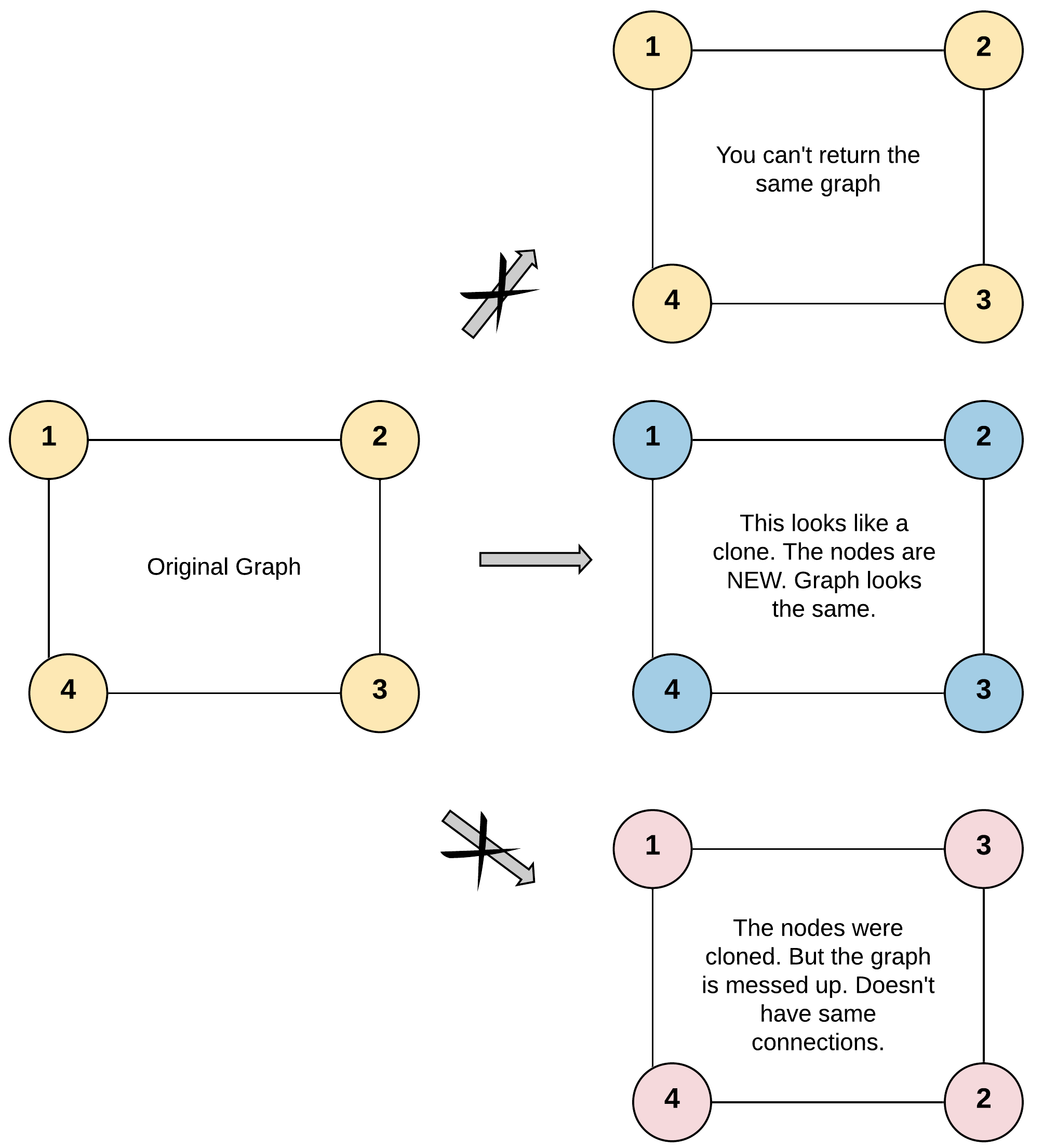
Input: adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] Output: [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] Explanation: There are 4 nodes in the graph. 1st node (val = 1)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4). 2nd node (val = 2)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3). 3rd node (val = 3)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4). 4th node (val = 4)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
Example 2:
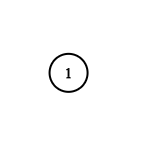
Input: adjList = [[]] Output: [[]] Explanation: Note that the input contains one empty list. The graph consists of only one node with val = 1 and it does not have any neighbors.
Example 3:
Input: adjList = [] Output: [] Explanation: This an empty graph, it does not have any nodes.
Example 4:
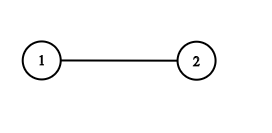
Input: adjList = [[2],[1]] Output: [[2],[1]]
Constraints:
1 <= Node.val <= 100Node.valis unique for each node.- Number of Nodes will not exceed 100.
- There is no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph.
- The Graph is connected and all nodes can be visited starting from the given node.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 | //C++: method1 80ms DFS /** * Definition for undirected graph. * struct UndirectedGraphNode { * int label; * vector<UndirectedGraphNode *> neighbors; * UndirectedGraphNode(int x) : label(x) {}; * }; */ class Solution { map<int, UndirectedGraphNode*> hash; public: UndirectedGraphNode *cloneGraph(UndirectedGraphNode *node) { if(!node) return NULL; UndirectedGraphNode *newNode = new UndirectedGraphNode(node->label); hash[node->label] = newNode; for(auto n:node->neighbors){ if(hash.count(n->label)==0){ cloneGraph(n); } newNode->neighbors.push_back(hash[n->label]); } return newNode; } }; ]]></script> //C++: method2 76ms /** * Definition for undirected graph. * struct UndirectedGraphNode { * int label; * vector<undirectedgraphnode *> neighbors; * UndirectedGraphNode(int x) : label(x) {}; * }; */ class Solution { public: UndirectedGraphNode *cloneGraph(UndirectedGraphNode *node) { if(!node) return node; unordered_map<int, UndirectedGraphNode *> hash; UndirectedGraphNode * newNode = new UndirectedGraphNode(node->label); hash[node->label] = newNode; queue<UndirectedGraphNode *> que; que.push(node); while(!que.empty()){ UndirectedGraphNode * t = que.front(); que.pop(); for(auto nb:t->neighbors){ UndirectedGraphNode *newNb = NULL; if(hash.count(nb->label)==0){ newNb = new UndirectedGraphNode(nb->label); hash[nb->label] = newNb; que.push(nb); } hash[t->label]->neighbors.push_back(hash[nb->label]); } } return newNode; } }; |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 | /* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public int val; public List<Node> neighbors; public Node() { val = 0; neighbors = new ArrayList<Node>(); } public Node(int _val) { val = _val; neighbors = new ArrayList<Node>(); } public Node(int _val, ArrayList<Node> _neighbors) { val = _val; neighbors = _neighbors; } } */ class Solution { Map<Integer, Node> map = new HashMap<>(); public Node cloneGraph(Node node) { if(node==null) return null; if(map.containsKey(node.val)) return map.get(node.val); Node newNode = new Node(node.val); map.put(node.val, newNode); for(Node n : node.neighbors){ newNode.neighbors.add(cloneGraph(n)); } return newNode; } } |
No comments:
Post a Comment